Real-Time Bidding 101: Guide for Advertisers and Publishers
The modern Ad Tech industry is at the cutting edge of technological progress. It uses the most advanced methods of data analysis and content delivery in order to present an advertising content to the user in the most precise and effective manner.
Ad Tech is fascinating because of all the things it does to present the most accurate content to the user. All the algorithms used to analyze user behavior match it with the present ad inventory and deliver the content — there is a lot of going on behind the scenes of the simple ads delivery operation.
What is Real-Time Bidding?
Real-time bidding approach was developed in the late 2000s out of ad networks dire need to utilize those parts of ad space inventory that were left unused for a variety of reasons, most notably lack of demand from the advertisers.
But instead simple utilization, Real-time bidding became a long-awaited shot in the arm to the ad industry that revitalized it and brought it to another level. Soon enough, it became apparent that the RTB architecture was very effective not only in filling the remnant inventory but in managing the entire inventory without much of a fuss.
At the moment, Real-time bidding is handling around 90% of all programmatic buying in digital advertisements which comprises a third in overall spending on digital ads.
How Real-time Bidding Works
Real-time bidding is one of those things that are best described in practical terms.
Let’s take a standard programmatic advertising situation. You know how it goes — you visit some site, watch some stuff and go on elsewhere but then there are some ads related to the stuff you’ve been watching on that site following you elsewhere presenting something that might be interesting to you. That’s retargeting in action. However, this is only a part of the story.
There is an entire sequence of events triggered by the users to visit the page that occurs in order to present ads to the user.
Here’s what happens. The user visit triggers a request from the publisher to the Supply-Side Platform that analyzes the request and transfers it to the Ad Exchange that connects with Demand-side platforms (AKA DSP) on behalf of the publishers and opens up an ad call bidding request to the available advertisers who enter the bidding process through the Demand-side platforms.
That’s where Real-time bidding occurs.
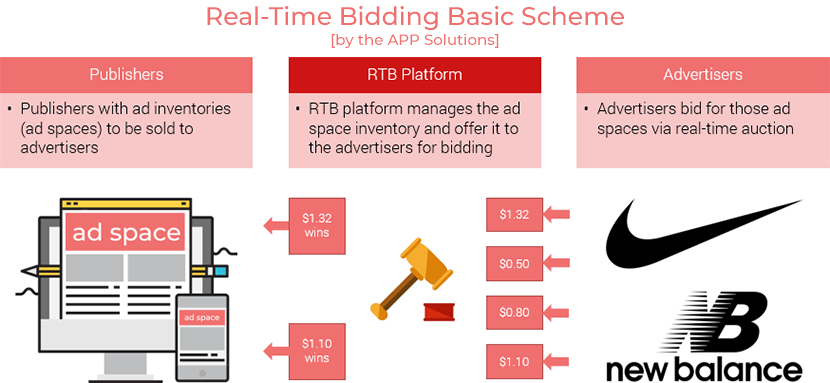
The process real-time bidding can be described as a fully-automated sequence of bids that works under a couple of pre-set algorithms with very distinct specifications regarding relevant audience segments, content, price ranges, and other elements.
Basically, Real-time bidding is an auction where advertisers try to outbid one another for the specific ad space. The endgame is usual — those who place the highest bid get the spot. The difference between traditional auction and RTB is that it all happens at lightning-fast speed. We’re talking about thousands of such auctions occurring at the span of milliseconds. Just think about it — a standard transaction in RTB usually takes about 100 milliseconds to happen.
Needless to say, in order to maintain such high proficiency in this process, one needs some serious scaling capacities.
Benefits of Programmatic Real-Time Bidding for Publishers and Advertisers
The introduction of Real-time bidding into digital advertising became a game-changing moment for the industry. It completely transformed the way advertisements are presented to the user and introduced a completely new business model for advertisers and publishers.
Overall, there are four major contributions of RTB protocol to ad tech industry.
Streamlined Process
The biggest innovation of Real-time bidding to ad tech operation is streamlining of the process to its bare essentials. Instead of sweep buying of the bunch of impressions, advertisers can do much more cost-effective per-impression buying process which makes the most out of ad budget due to increased flexibility of the process.
On the other hand, RTB turned the laborious and often tangled process of placing ads on relevant spaces into the more automated realm.
The whole meticulous process of sorting ad spaces and checking its relevance and credibility is relegated to the automated platforms that do all the dirty job within a blink of an eye. Now — all it takes to make an effective ad tech operation is to set the requirements and adjust them according to the incoming results.
Superior Efficiency & Flexibility
Campaign Performance and ability to adjust campaign accordingly is one of the strategic priorities in an ad tech operation. RTB algorithm brings additional flexibility to the mix.
The thing is — Real-Time Bidding allows managing the campaign as if it was a real-time strategy — as it goes. This gives a lot of space to maneuver and analyze the efficiency of ads with certain audience segments and ad spaces. This leads to constant improvement of the strategy to its most effective state. Real-time factor reduces the waste and impact of wrong decisions to a minimum. This also makes whole advertising turnaround much faster.
Price Optimization
Keeping an ad budget under control is one of the biggest challenges of maintaining an ad tech operation. Real-time bidding allows to automate that peculiar aspect and keep the things within reasonable boundaries by setting specific price-requirements.
The other important aspect of budget control is price optimization which can also be automated in correlation with the campaign performance results via real-time analytics. This allows to maximize the revenue and concentrate an effort on the most lucrative audience segments.
Anti-fraud Protection
Ad Fraud is one of the biggest problems in the Advertising industry. Each year it eats up a significant part of ad spending of advertisers. Given the lightning-fast nature of RTB operation — it seems like tailor-made environment for massive fraudulent activity.
However, with the increased automation of the process and constantly adaptable campaigns — the overall influence of ad fraud is minimized. The fact of the matter is — modern fraud detection system cut off the majority of fraudulent sources long before they get into the mix.
In addition to that, campaign analytics can expose any semblance of suspicious activity (for example, anomalous click-through rate) and take them out of charging due to fraudulence.
Challenges of Real-Time Bidding
Efficiency Scaling
Scalability is one of the biggest challenges of ad tech. Since the whole operation needs to maintain high-speed reaction and adjustment to the incoming information — the scaling capacities of a DMP must be nothing less than exquisite, which is a challenge considering how much information goes through and how fast it must be processed.
The solution for the scalability challenges lies in cloud computing. For example, such platforms as Google Cloud, AWS and Azure offer autoscaling features that take a lot of headache out of an equation.
Prediction Mechanism
The prediction mechanism is one of the most important elements of an ad tech operation and as such it must be tailor-made to the requirements of your operation and deliver the results according.
In the center of the prediction mechanism is a combination of supervised machine learning algorithms that includes classification, regression process.
These processes sort out and recognize the incoming data and subsequently calculate possible outcomes and their likeness of accordingly. These mechanisms allow predicting the possibilities and opportunities for conversions with particular audience segments on specific ad spaces.
In addition to that, there is an additional algorithm involved for the purposes of user modeling and subsequent that adapts to the results of the campaign.
Ad Fraud Detection
While overall Real-time Bidding is much more controlled operation than other types of digital advertising, its velocity (i.e. too much too fast) makes it much more ad fraud-prone. In order to shut off any semblance suspicious activity out of the equation and minimize the influence of ad fraud on an ad campaign.
The challenge comes with identifying and preventing ad fraud activity. The thing is — ad fraud is constantly evolving and each day brings new challenges.
However, there are certain patterns that can be easily identified in case of bot activity. With the little help of certain algorithms, bots can be shut off from the system and their activity will do nothing more than shake the air between the ones and zeroes.
Bid Optimization
The process of bidding is a balancing act — you need to know approximate ranges of your spending and plan the whole thing in relatively long terms. The whole bidding process is organized around the campaign goals — how many clicks or conversions are expected and what can be considered as a success.
In addition to that, you need to assess the effectiveness of the spending on a particular type of ads and consider different options for a variety of scenarios.
The key thing for an effective bid optimization is predictive analytics. The stats give you the bigger picture of your campaign in real time and that will help you to adjust bidding algorithms accordingly on the go without experiencing an aftermath of past ineffective decisions.
Budget Control
The other important element of RTB optimization is budget control. The fact of the matter is — there must be boundaries of how much can for certain types of ads and over certain periods of times.
Here’s how works: if an ad of a specific type delivers good results on a specific ad space — there are more of such ads placed and if a specific type of ad fails to deliver in a particular ad space — it ceases and resources are relocated elsewhere.
Conclusion
Real-time bidding is one of those technologies that require a clear understanding of its possibilities and distinct boundaries to work in. We’ve covered the basics of the concept and broke down all the major challenges that come with the implementation of this process – but in the end, it all comes to business analysis during the inception phase to make sure all the RTB algorithms and other technologies involved are chosen wisely.
