Cloud computing is a kind of infinite pool of possibilities. In one way or another – anything is possible with cloud computing in the mix. This technology makes everything more convenient and less troublesome. Cloud computing helps development teams in solving the following issues:
- Storing a massive amount of data
- Training machine learning algorithms
- Constructing a practical business framework
- Automating and orchestrate the routines
- Handling large workloads
Cloud elasticity and scalability are amongst the integral elements of cloud computing. Despite its widespread use, there is a lot of confusion regarding what is doing what and how exactly. This article will explain what the difference between scalability and elasticity in cloud computing.
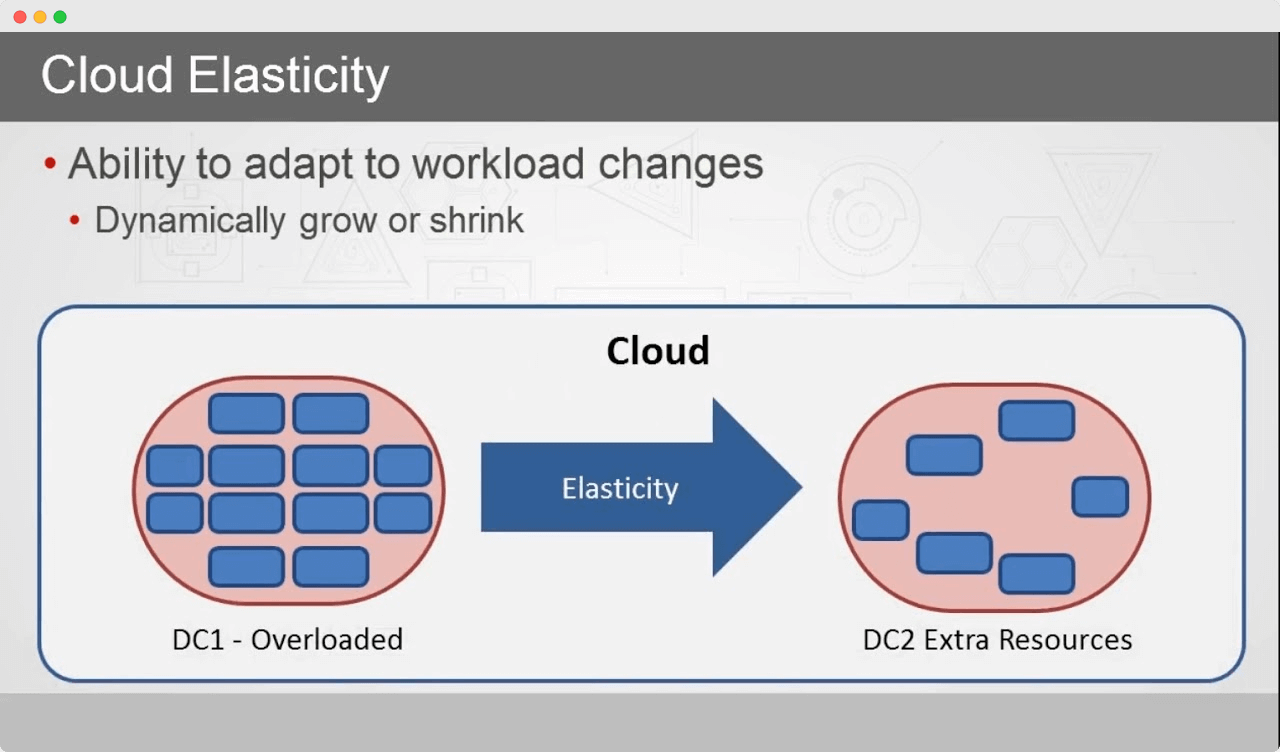
What is Cloud Elasticity?
[Source]
Сloud elasticity is a system’s ability to manage available resources according to the current workload requirements dynamically.
This is a vital feature of a system infrastructure. It comes in handy when the system is expected to experience sudden spikes of user activity and, as a result, a drastic increase in workload demand.
Thanks to the pay-per-use pricing model of modern cloud platforms, cloud elasticity is a cost-effective solution for businesses with a dynamic workload like streaming services or e-commerce marketplaces.
Various seasonal events (like Christmas, Black Friday) and other engagement triggers (like when HBO’s Chernobyl spiked an interest in nuclear-related products) cause spikes in customer activity. These volatile ebbs and flows of workload require flexible resource management to handle the operation consistently.
Usages of this cloud infrastructure functionality include:
Streaming Services. Netflix is dropping a new season of Mindhunter. The notification triggers many users to get on the service and watch or upload the episodes. Resource-wise, it is an activity spike that requires swift resource allocation. Thanks to elasticity, Netflix can spin up multiple clusters dynamically to address different kinds of workloads.
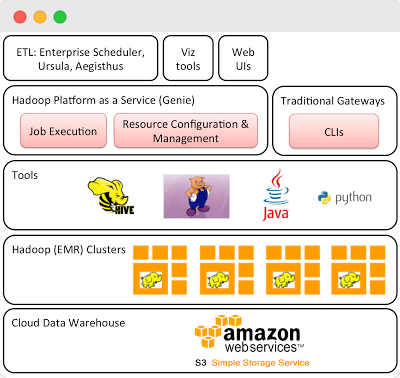
[Netflix architecture leverages the elasticity of the cloud to scale up and down, source]
E-commerce applications. Amazon has a Prime Day event with many special offers, sell-offs, promotions, and discounts. It attracts a massive amount of customers to the service who are doing different activities. Actions include searching for products, bidding, buying stuff, writing reviews, rating products. This diverse activity requires a very flexible system that can allocate resources to one sector without dragging down others.
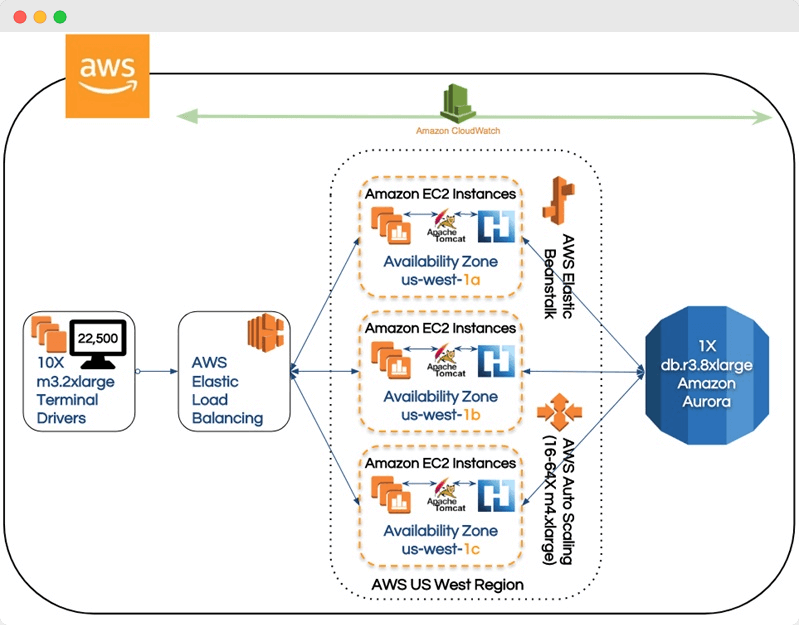
[Amazon infrastructure event management, source]
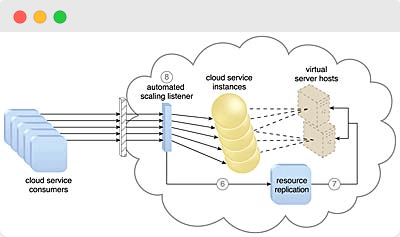
What is Cloud Scalability?
[Source]
System scalability is the system’s infrastructure to scale for handling growing workload requirements while retaining a consistent performance adequately.
Unlike elasticity, which is more of makeshift resource allocation – cloud scalability is a part of infrastructure design.
Scalability is one of the prominent features of cloud computing. In the past, a system’s scalability relied on the company’s hardware, and thus, was severely limited in resources. With the adoption of cloud computing, scalability has become much more available and more effective.
Automatic scaling opened up numerous possibilities for implementing big data machine learning models and data analytics to the fold. Overall, Cloud Scalability covers expected and predictable workload demands and handles rapid and unpredictable changes in operation scale. The pay-as-you-expand pricing model makes the preparation of the infrastructure and its spending budget in the long term without too much strain.
There are several types of cloud scaling:
- Vertical scale, e.g., Scale-Up – can handle an increasing workload by adding resources to the existing infrastructure. It is a short term solution to cover immediate needs.
- Horizontal scale, e.g., Scale-Out – expands the existing infrastructure with new elements to tackle more significant workload requirements. It is a long term solution aimed to cover present and future resource demands with room for expansion.
- Diagonal scale is a more flexible solution that combines adding and removing resources according to the current workload requirements. It is the most cost-effective scalability solution by far.
Scalability is an essential factor for a business whose demand for more resources is increasing slowly and predictably.
Examples of cloud scalability include:
Call Centers. The typical call center is continuously growing. New employees need more resources to handle an increasing number of customer requests gradually, and new features are introduced to the system (like sentiment analysis, embedded analytics, etc.). In this case, cloud scalability is used to keep the system’s resources as consistent and efficient as possible over an extended time and growth.
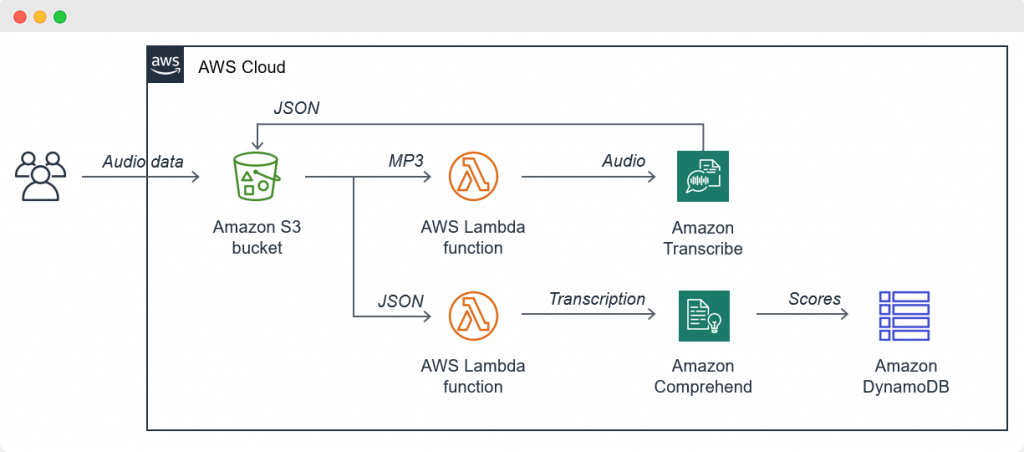
[Application architecture for call centers with cloud scalability, source]
Chatbots are another example of cloud scalability in action. Advanced chatbots with Natural language processing that leverage model training and optimization, which demand increasing capacity. The system starts on a particular scale, and its resources and needs require room for gradual improvement as it is being used. The database expands, and the operating inventory becomes much more intricate.
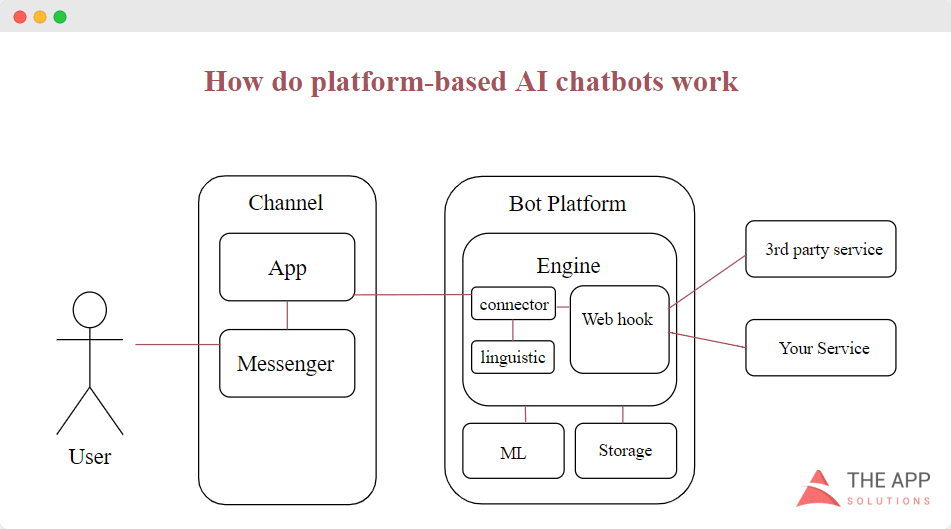
Consequently, cloud scalability is integral for cloud-based services such as:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) – Amazon EC2 or Google Compute Engine
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) – Magento Commerce Cloud or AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Storage-as-a-Service (STaaS) – Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, and the likes
- Data-as-a-Service (DaaS) – customer relationship platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot, ERP applications
- Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS) – AWS SimpleDB, Rackspace, Oracle, MongoDB
What is the difference between Elasticity and Scalability?
In the grand scheme of things, cloud elasticity and cloud scalability are two parts of the whole. Both of them are related to handling the system’s workload and resources.
The fundamental concept of the two is adaptability. It refers to the system environment’s ability to use as many resources as required.
The difference between elasticity vs. scalability lies in their functions:
- Cloud Elasticity is a tactical resource allocation operation. It provides the necessary resources and capacity required for the current task and handles varying loads for short periods. For example, running a sentiment analysis algorithm, doing database backups, or just taking on user traffic surges on a website.
- Cloud Scalability is a strategic resource allocation operation. Scalability handles the scaling of resources according to the system’s workload demands.
Advantages of Cloud Elasticity and Scalability
Both features occur behind the scenes and make the system workflow smooth and seamless. As you can see, it is similar to the “think global – act locally” approach of social activists. The main benefits of elasticity and scalability are the following:
Cost-effectiveness
Cloud scalability and elasticity features constitute an effective resource management strategy:
- The pay-per-use model is the best solutions for sudden surges of workload demand (vital for streaming services and marketplaces)
- The pay-as-you-expand model allows to plan out gradual capacity growth of the infrastructure in sync with growing requirements (convenient for ad tech systems)
Consistent performance
Elasticity and scalability features operate resources in a way that keeps the system’s performance smooth, both for operators and customers.
Service availability
Scalability enables stable growth of the system, while elasticity tackles immediate resource demands.
Download Free E-book with DevOps Checklist
Download NowElasticity vs. scalability in cloud computing: The final word
Modern business operations live on consistent performance and instant service availability.
Cloud scalability and elasticity handle these two business aspects in equal measure.
- Cloud scalability is an effective solution for businesses whose needs and workload requirements are increasing slowly and predictably.
- Cloud elasticity is a cost-effective solution for organizations with dynamic and unpredictable resource demands.
These features make scalability and elasticity a viable instrument for the company to hold its ground, grow steadily, and gain a competitive advantage.
Related articles:
