- Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0 and their differences
- What is Web 1.0?
- What is Web 2.0?
- Features of Web 2.0
- What is Web 3.0?
- Features of Web 3.0
- Difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
- Content presentation principle
- Content Ownership Principle
- Application types
- User acquisition paths
- Technologies
- Key Takeaways
To whatever terms, the word “web” is applied! Anything that somehow refers to the Internet can be a “web” – a site, a page, access, security, a camera… It is not surprising because the word “web” is a component of the three “great” WWW – World Wide Web – connected by websites on the network. But this prefix also applies to numbers. This is the forgotten Web 1.0. And Web 2.0, which is definitely on everyone’s lips because it occupies a dominant position. And, of course, Web 3.0, which came into use not so long ago but is widely used in certain circles, while still very timidly displacing its predecessor.

Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0 and their differences
Let’s deal with all these concepts to say goodbye to uncertainty once and for all! What are the differences between Web 1.0 vs. Web 2.0 vs. Web 3.0?
Web 1, 2, and 3.0 are evolutionary services that determine how users interact with and within the Internet. It all started as one-way communication from the network to users. It came to decentralized mechanisms for storing and transmitting data, which have come to a thorny path, just like silent movies turned into augmented reality movies. Each stage had its meaning and was relevant and most convenient at a particular moment in the Internet’s development.
How To Make A Personal Finance App
What is Web 1.0?
Web 1.0 is the first iteration of the Internet, dating back to the 90s with the first browsers. The most accessible and easy to understand. In this approach, the network is considered a source of information, and the user is its absorber. They were just directory, static web pages.
In those days, email was considered happiness. But, at the same time, the possibilities for creating content were very scarce – mainly read-only.

What is Web 2.0?
Web 2.0 is the second generation of interoperable Internet services. If earlier the user could only consume content, now he has the opportunity to independently produce it and exchange it with other site users (user-generated content). This became the basis for the commercialization of the Internet – entire areas of activity were en masse digitized, otherwise, they risked dying. That is; retail, banking, advertising, media, and entertainment…
It also became the basis for social networks as virtual communication platforms. This can include any interaction from written blogs to audio podcasts, from RSS to commonplace tags that allow you to find content based on your interests more efficiently. Prime examples of Web 2.0 are Apple, Amazon, Google, and other FAANG representatives.

Features of Web 2.0
- Access to web content from mobile devices, tablets, TVs, consoles, and even a kettle connected to the Internet
- Dynamic content (as opposed to static first-generation web pages), which is designed to work in CTA mode
- User participation in content creation – users not only share and comment on articles and videos but also produce them themselves
- In the process of data transmission, there is a specific “intermediary” – a controlling platform
- Development of API for interaction between different programs
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the third generation of Internet services that focuses on decentralizing processes and eliminating any middleman trying to take control of everyone and everything. In addition, Web 3.0 uses encryption and distributed ledger technology to address the trust issues present with Web 2.0. But decentralized Web 3.0 is not only about security but also about more effective interaction due to artificial intelligence.
This new move is sometimes called the Web 2.0 killer, although this is clearly premature. However, it cannot be denied that with the advent of this technology, many established processes will change.
How Does Blockchain Amplify Adtech Industry
Although not everything is so cloudless in Web 3.0, with the loss of control, it will become impossible to combat negative phenomena such as cybercrime, incitement to hatred, and disinformation, which are now increasingly challenging to deal with. Not to mention the laws because it is not completely clear which country’s judicial authorities will have to be involved in disputes. And the scalability of transactions in Web 3.0 is still insignificant, which significantly slows down processing.

Features of Web 3.0
- Artificial intelligence, which selects the most relevant options for information (search engines are actively engaged in it, reducing the role of organic search results)
- Semantic Web or an option that allows machines to better interact with humans by understanding and interpreting the meaning of human words
- Use of 3D images and graphics
- A new level of security and privacy through decentralization (blockchain) – freedom from censorship and surveillance due to the lack of a control center – distributed ledger, and decentralized finance (Defi)
What You’re Paying For Or How Ads.Txt Helps To Fight Adtech Fraud
Difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 are consistent technologies with a common background, but they solve their problems in different ways. The main difference can be described as the fact that Web 2.0 aims to read and write content, and Web 3.0 at the essence (Semantic Web). However, the latter is even better than before, applying technologies to exchange information between Internet users while also increasing security.
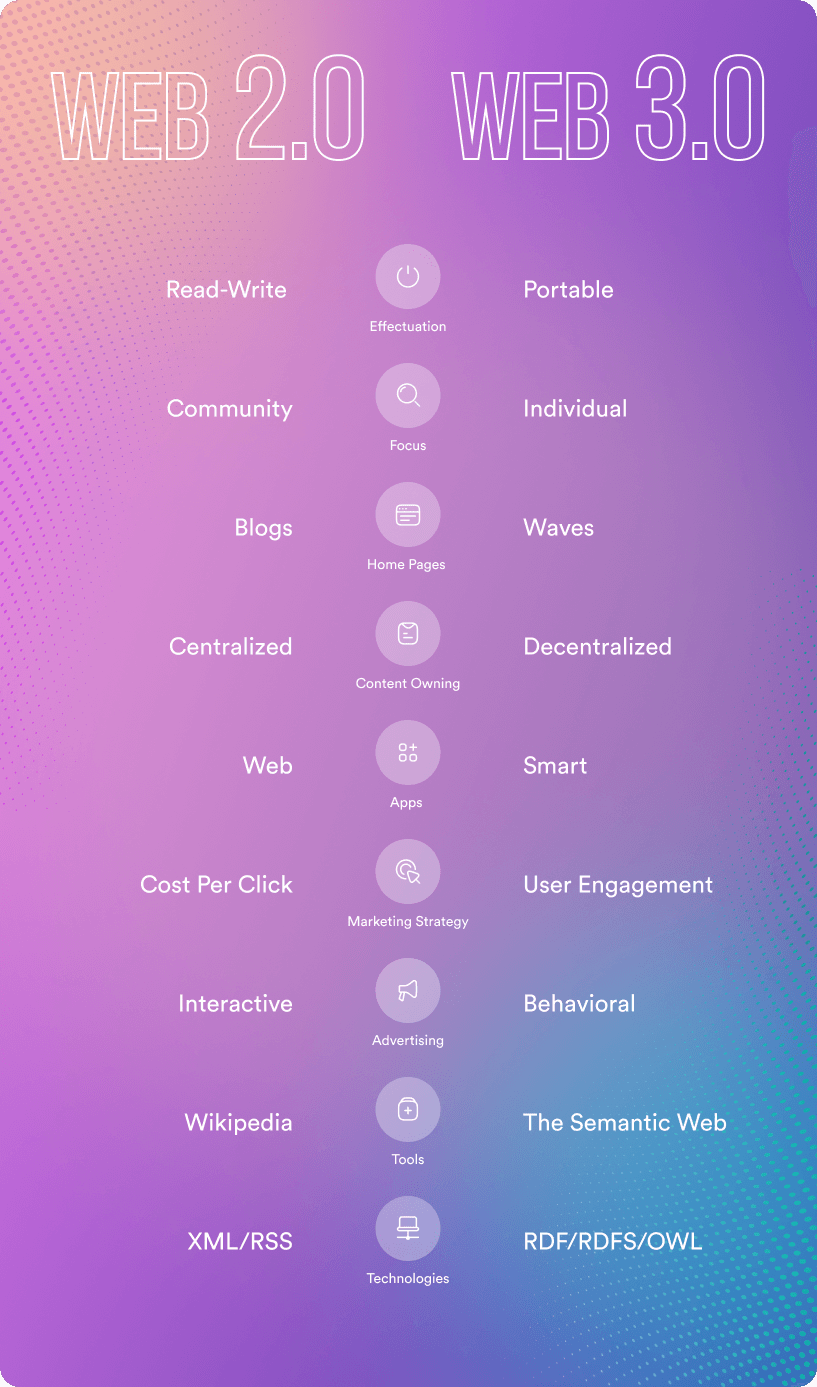
Content presentation principle
In other words, the main goal of Web 2.0 was to unite people around the data they were interested in, and Web 3.0 combines this data in meaning while increasing the trust in information thanks to the notorious decentralization. Thus, the communities that were naturally created with Web 2.0, with Web 3.0 disintegrate to personalize information and expand opportunities and rights. This leads to the following difference.
Content Ownership Principle
With Web 2.0, the network itself assumed responsibility for storing information, which caused specific difficulties with access and fears for the safety and confidentiality of online data. This problem was solved by Web 3.0 with the flexibility of data exchange, which can now exist at many points at once. However, Web 2.0 transfers are still faster than Web 3.0.
In Web 2.0, computers use HTTP in the form of unique web addresses to find information that is stored in a fixed location, usually on a single server. However, in Web 3.0, since information will be found based on its content, it can be stored in several places at the same time and, therefore, be decentralized; it is certainly not in the interests of the Internet giants.
The degree of centralization/decentralization of the network is in the range; no network is entirely controllable or completely independent.
Challenges and Limitations of Web 3.0 Adoption
Web 3.0 might be a new round in web technology evolution that promises to bring numerous benefits, such as
- Enhanced data privacy and control through improved blockchain technology and cryptographic techniques,
- Decentralization of traditional systems that eliminates many error-prone and time-consuming intermediaries,
- Personalized and customized user experiences through accurate data collection and analysis.
However, it also comes with its limitations and challenges that slow down its progress and might even potentially diminish its advantages. Here are the most popular constraints that must be taken into account:
Complexity of the technology. This raises many tiny yet critical concerns, such as a steep learning curve for users, difficulty in navigation, and the tricky introduction of high-end features in complex systems.
Slow scalability. Due to complexity, applications powered by Web 3.0 technologies, especially those relying on blockchain and cryptography, are difficult to scale. It might take time and special human resources that potentially hinder performance and user experience.
Privacy concerns. Web 3.0 is infamous for its data breaches, surveillance issues, predisposition to cyber-attacks, and the misuse of personal information, caused by decentralized data storage and the blockchain system.

Application types
For Web 2.0, these are podcasts, blogs, and video sites. In general, any type of information fits the description of self-production of content and user communication. For Web 3.0, these will be AI and ML-powered applications (dApps) such as multi-user virtual environments, 3D portals, and integrated games.
User acquisition paths
Interactive advertising works with Web 2.0, while behavioral advertising works with its “successor.” In the first case, there is a certain moderation due to the presence of a controlling body; in the second, it is impossible.
Technologies
Compared to the first, the second iteration had to take a big step forward to meet new challenges, among which the main one was to stimulate the exchange of content, not just its consumption. AJAX and JavaScript, CSS3, and HTML5 are most often named among the technologies specific to Web 2.0. And then, there was a boom in the development of AI, which could not but affect Web 3.0, which was supposed to serve as a reliable “shelter” of information on the one hand and a content quality booster on the other. The leading technologies behind Web 3.0 include machine learning, deep learning, semantic web, and decentralized protocols.
Key Takeaways
Of course, Web 3.0 is an important step towards progress, but it is not perfect, so it is too early to bury Web 2.0. At the moment, the two strategies coexist perfectly. While the second still dominates, the third iteration is not far off. We at The APP Solutions are friends with both technologies and are ready to work with the projects you propose to us.
Credits to Depositphotos
