What Is Pattern Recognition and Why It Matters? Definitive Guide
Because of big data and machine learning technologies’ emergence, a lot of data became available that was previously either deduced or speculated. This data, rooted in more credible sources, provided the means to use more complex methods of data analysis to gain value-added benefits for the business.
In other words, now that we “knew more,” we moved from the goal of getting information itself to analyzing and understanding the data that was already coming to us.
Of all the tools used in Big Data, pattern recognition is in the center. It comprises the core of big data analytics – it gets the juice out of the data and uncovers the meanings hidden behind it.
Pattern recognition gives a strategic advantage for the company which makes it capable of continuous improvement and evolution in the ever-changing market.
What is Pattern Identification?
Pattern Recognition is the process of distinguishing and segmenting data according to set criteria or by common elements, which is performed by special algorithms.
Since pattern recognition enables learning per se and room for further improvement, it is one of the integral elements of machine learning algorithm.
Christopher Bishop in his seminal work “Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning” describes the concept like pattern recognition deals with the automatic discovery of regularities in data through the use of computer algorithms and with the use of these regularities to take actions such as classifying the data into different categories.
In other words, pattern recognition is identifying patterns in data. These patterns tell the training data stories through ebbs and flows, spikes, and flat lines.
The data itself can be anything:
- Text
- Images
- Sounds
- Sentiments, and others.
Any information on the sequential nature can be processed by pattern recognition algorithms, making the sequences comprehensible and enabling their practical use.
Advanced Trends in Pattern Recognition for Business Applications
Enabling accurate and relevant data-driven decisions and pattern recognition for business applications offers numerous benefits for companies. It improves efficiency, boosts workflows and collaboration, decreases development time and costs, and helps companies keep up with the mainstream. If you are one of those who have already recognized all the advantages of this approach, here are some advanced trends that you can follow.
- Integration with Edge AI. The AI models that tend to apply their algorithms on devices close to where data is generated are getting increasingly popular these days as they decrease the need for cloud resources, keep operational expenses down, and boost the efficiency of the system.
- Self-learning systems. Coming with continuous learning loops, modern artificial intelligence systems for recognition quickly analyze and adapt to new data. They provide personalized recommendations, anticipate trends, predict maintenance, and help to detect malicious activity.
- Cross-modal pattern recognition. As users’ data comes in different formats, it is becoming crucial to use tools that effectively inspect and examine text, images, sound, video, and sensor information for rich pattern detection.
Pattern Recognition Techniques
There are three main models of pattern recognition:
- Statistical Pattern Recognition: to identify where the specific piece belongs (for example, whether it is a cake or not). This model uses supervised machine learning;
- Syntactic/Structural: to define a more complex relationship between elements (for example, parts of speech). This model uses semi-supervised machine learning;
- Template Matching: to match the object’s features with the predefined template and identify the object by proxy. One of the uses of such a model is plagiarism checking.
Introduction to Pattern Recognition
While the majority of pattern recognition in artificial intelligence operations is self-descriptive, there is a lot going on underneath.
Overall, there are two major parts of pattern recognition algorithms:
- explorative – used to recognize commonalities in the data;
- descriptive – used to categorize the commonalities in a certain manner;
The combination of these two elements is used to extract insights out of the data, including the use in big data analytics. The analysis of the common factors and their correlation uncovers details in the subject matter that may be critical in understanding it.
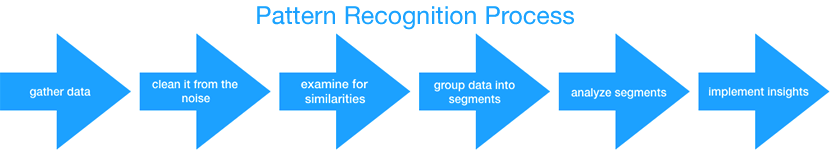
The process itself looks like this:
- Data is gathered from its sources (via tracking or input)
- Data is cleaned up from the noise
- Information is examined for relevant features or common elements
- These elements are subsequently grouped in specific segments;
- The segments are analyzed for insights into data sets;
- The extracted insights are implemented into the business operation.
Use Cases for Pattern Recognition

Stock Market Forecasting, Audience Research – Data Analytics
Pattern Recognition technology and Data Analytics are interconnected to the point of confusion between the two. An excellent example of this issue is stock market pattern recognition software, which is actually an analytics tool.
In the context of data analytics, pattern recognition is used to describe data, show its distinct features (i.e., the patterns themselves), and put it into a broader context.(Read more in our article about Data Analytics and Data Mining.)
Let’s look at two prominent use cases:
- Stock market forecasting – pattern recognition is used for comparative analysis of the stock exchanges and predictions of the possible outcomes. YardCharts use this pattern recognition analysis.
- Audience research – pattern recognition refers to analyzing available user data and segmenting it by selected features. Google Analytics provides these features.

Text Generation, Text Analysis, Text Translation, Chatbots – Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (aka NLP) is a field of Machine Learning focused on teaching machines to comprehend human language and generate its messages. While it sounds like hard sci-fi, in reality, it doesn’t deal with the substance of communication (i.e., reading between the lines) – it only deals with what is directly expressed in the message.
NLP breaks the text to pieces, finds the connections, and then constructs its variation. The process starts with differentiating the sentences; then it sorts out the words and parts of the speech where they belong and finally defines the ways these words can be used in a sentence.
To do that, NLP uses a combination of techniques that includes parsing, segmentation, and tagging to construct a model upon which the proceedings are handled. Supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms are involved in this process at various stages.
NLP is used in such fields as:
- Text analysis – for content categorization, topic discovery, and modeling (content marketing tools like Buzzsumo use this technique);
- Plagiarism detection – a variation of text analysis focused on a comparative study of the text with the assistance of the web crawler. The words are broken down into tokens that are checked for matches elsewhere. The exemplary tool for this is Copyscape.
- Text summarization and contextual extraction – finding the meaning of the text. There are many online tools for this task, for example, Text Summarizer;
- Text generation – for chatbots and AI Assistants or automated content generation (for example, auto-generated emails, Twitterbot updates, etc.);
- Text translation – in addition to text analysis and word substitution, the engine also uses a combination of context and sentiment analysis to make closer matching recreation of the message in the other language. The most prominent example is Google Translate;
- Text correction and adaptation – in addition to correcting grammar and formal mistakes, this technique can be used for the simplification of the text – from the structure to the choice of words. Grammarly, a startup founded by two Ukrainians in Kyiv, Ukraine, is one of the most prominent examples of such NLP pattern recognition uses.

Document Classification and Signature Verification – Optical Character Recognition
Optical Character Recognition (aka OCR) refers to the analysis and subsequent conversion of the images considered as alphanumeric text into the machine-encoded text.
How to make your IT project secured?
Download Secure Coding GuideThe most common source of optical characters are scanned documents or photographs, but the thing can also be used on computer-generated unlabeled images. Either way, the OCR algorithm applies a library of patterns and compares them with the available input document to mark up the text and construct these. These matches are then assessed with the assistance of language corpus and thus perform the “recognition” itself.
In the heart of OCR is a combination of pattern recognition system and comparative algorithms attached to the reference database.
The most common uses of OCR include:
- Text Transcription is the most basic process. The text is presented in recognizable characters is recognized and transposed into the digital space. This technology is well-presented on the market. A good example might be ABBYY Fine Reader.
- Handwriting Recognition is a variation of text transcription with a more significant emphasis on the visual element. However, this time, the OCR algorithm uses a comparative engine to process the handwriting sample. A good example of this is Google Handwriting Input. While this technique’s primary goal is to the transcript, it is also used to verify signature and other handwriting samples (for example, for signing contracts or handwritten will);
- Document Classification involves deeper processing of the document with a bigger focus on its structure and format. This technique is used for digitization of the paper documents and also for the reconstruction of the scattered elements of the damaged documents (for example, if the thing is shredded or the ink is partially blurred). Parascript is a product that provides such services for document classification.

Visual Search, Face Recognition – Image Pattern Recognition
Image Recognition is a variation of OCR aimed at understanding what is on the picture. In contrast with OCR, image recognition to recognize what is depicted on the input images during image processing. Basically, instead of “recognizing” is “describes” the picture so that it would be searchable and comparable with the other images.
The main algorithms at work in image recognition are a combination of unsupervised and supervised machine learning algorithms.
The first supervised algorithm is used to train the model on the labeled datasets, i.e., examples of the depiction of the objects. Then the unsupervised algorithm is used to explore an input image. After this, a supervised algorithm kicks in and classifies the patterns as related to the particular category of objects (for example, an ink pen).
There are two main use cases for Image Recognition:
- Visual Search features are widely used in Search Engines and eCommerce marketplaces. It works the same way as an alphanumeric search query only with images. In both cases, image recognition constitutes a part of the equation. The other part is image metadata and also additional textual input. This information is used to increase the efficiency of the results and to filter the selection of options according to the context. For example, such technologies are widely applied by Google Search and Amazon.
- Face Detection is widely used in social network services, such as Facebook and Instagram. The same technology is used by law enforcement to find a person of interest or criminals on the run. The technical process behind face detection is more intricate than simple object recognition. To recognize the appearance of a certain person, the algorithm needs to have a specialized labeled sample set. However, due to privacy limitations, these features are usually optional and require user consent. One of the better-known examples of this technology is VeriLook SDK.

AI Assistants, Speech-To-Text, Automatic Subtitling – Voice Recognition
The sound is an equally important source of information as any other. With the rapid development of machine learning algorithms, it became possible to use it in providing basic services.
In essence, voice recognition works on the same principles as OCR. The only difference is the source of information.
Voice and sound recognition are used for the following purposes:
- AI Assistants / Personal Assistant apps use natural language processing to compose the message and an additional database of sound samples to perform the message. For example, Google Assistant;
- Sound-based Diagnosis – uses the comparative database of sounds to detect anomalies and suggest a possible cause and ways of fixing it. Commonly used in the automobile industry to inspect the state of the engine or the parts of the vehicle.
- Speech-to-text and text-to-speech transformation use a comparative database of samples, OCR engine, and speech generation engine. Outside of AI assistants, it is also used to narrate written text (for example, this feature is available on Medium);
- Automatic Caption addition involves speech-to-text recognition and subsequent image overlay to present the text on the screen (for example YouTube or Facebook automatic subtitling features).

Audience Research, Customer Service, Prescription, Machine Learning, Recommendation – Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment Analysis is a subset of pattern recognition that takes an extra step to define its nature and what it can mean. In other words, it tries to understand what is behind the words – the mood, opinion, and, most importantly, an intent. It is one of the more sophisticated types of pattern recognition.
Sentiment analysis for business solutions can be used to explore the variety of reactions from the interactions with different kinds of platforms. To do that, the system uses unsupervised machine learning on top of the basic recognition procedure.
The assumptions of the sentiment analysis are usually grounded incredible sources such as dictionaries, but it can also include more customized databases depending on the context of the operation.
The use cases for sentiment analysis include:
- Audience Research, content optimization, customer relationship platforms – used for the further definition of the audience segments, their interaction with the content, and analysis of the sentiments regarding it. It also contributes to the further optimization of the content. Such features are now tried out by Salesforce’s Einstein platform services.
- Service Support – provides assistance in defining the nature of the query (whether it is positive or negative, combative, or poorly defined). This feature is commonly used in AI assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Cortana;
- Prescription/Recommendation – used to predict the content of interest for the particular user. The suggestion may be augmented by the queries and past history of service use. The best examples are Netflix with their “you might also like” and Amazon with “people also buy”;
In Conclusion: Pattern Recognition Systems
Pattern recognition is the key to the further evolution of computational technology. With its help, big data analytics can progress further and we can all benefit from the machine learning algorithms getting smarter and smarter.
As you can see, pattern recognition can be implemented in any kind of industry because where there is data, there are similarities in the data. Therefore, it’s wise to consider the possibility of implementing this technology into your business operations to make them more efficient.
