Recently our team decided to brush up on the experience with augmented reality and geolocation, so we have created a custom-designed Augmented Reality navigation application for cafes and restaurants in the city aimed at foreigners.
The application shows real-time distance and time of travel for a particular spot and shows important information about a particular place of interest.
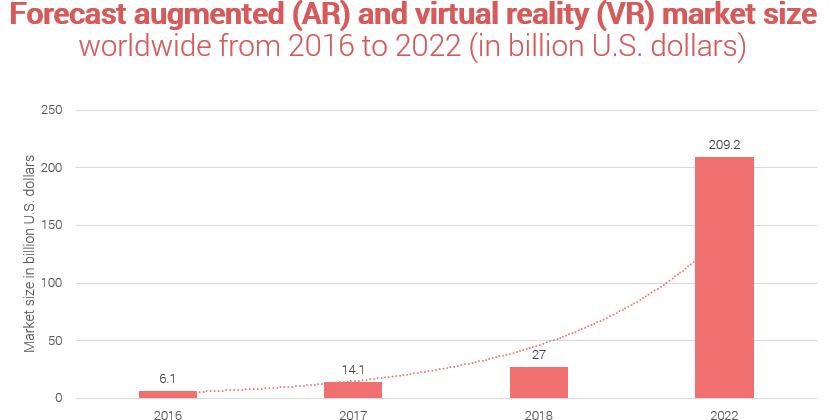
The augmented (as well as virtual) reality s market is growing rapidly and it’s only a question of time when it would skyrocket. According to Statista, it’s going to happen quite soon: in 2022.
Project Overview
Sometimes, all it takes to start a project is the sheer desire to learn something new. Places started like that. At the very start, it wasn’t even supposed to be an application – just a learning exercise for developers to get a grip on augmented reality. However, as time went by, it evolved into a fully-fledged application.
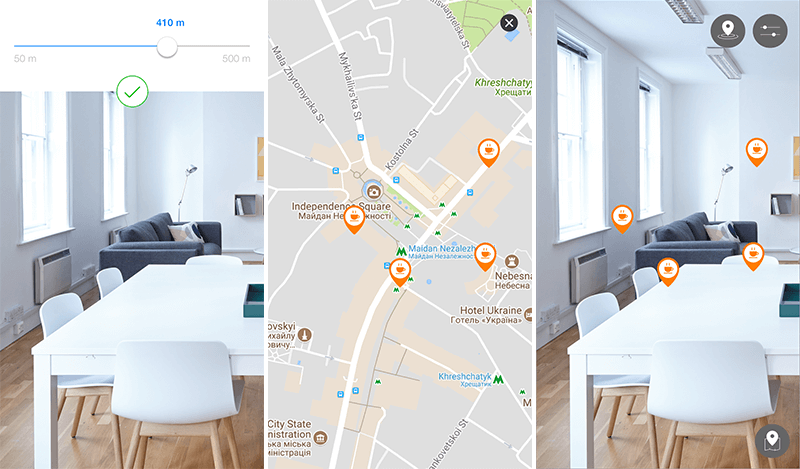
Places mobile app is specifically designed for those who don’t know the whereabouts of the city but want to visit its local restaurants. It is part discovery app and part navigation app. Places AR app consists of two modes:
- Map mode where the user can see the entire area with pins;
- AR mode where the user can see pins in accordance with the actual distance between user and place.
The application provides everything one needs to know about the particular place – where it is situated, what kind of meals it serves, price range, etc. The app also shows approximate distance and travel time towards a selected spot.
In its current incarnation, the project required not a just tech-savvy team with solid expertise both in augmented reality and geolocation but also thorough business analysis and thought-through business model in order to launch successfully launch an app.
Our team was responsible for the project from start to finish. It was a result of refining of the skills gone so far it evolved into a full-on application.

Camera Calibration
One of the biggest challenges our team had faced during the development of the project was adjusting the calibration and orientation of the camera phone in order to correctly depict pins and their distances. The challenge is that you need to know where the user is and how the phone is orientated as he walks around.
Due to the imperfections of mapping real-world device moves into a 3D scene coordinate system in ARKit, this procedure needed additional solutions and thorough testing. In order to pull this off, we set up the configuration in such a manner that ARKit would align the world both with gravity and direction (with regards to True North) which allowed a more accurate definition of the camera’s orientation on the application.
In order to avoid mistakes in the placement of the pins, we have developed an automated calibration solution that extracts pixel coordinates of the pinpoints and uses map coordinates to create correspondence. This provides precise placement of the pins on the screen with a realistic depiction of distance.
Coordinate Transmitting
Another big challenge was to maintain transmission of coordinates from Google Maps / Places to the phone so that it would be adequately depicted through the camera. We needed to secure the correct depiction of scale, distance, and vertical axis.
We created a link between the user’s device and Google Maps / Places so that it would depict nearby pins with correct distances. Complex calculations and vector transformations had been applied to place location pins in proper places.
Each place as seen on Google Places was transformed into the local 3D coordinate system on the device.
Read also: Business Cases for AR Navigation
Intuitive Design
In comparison with other challenges, the design wasn’t that big of a deal, but it definitely was a challenge of its own. Design requirements for such kind of project are extremely minimal and that required a completely different approach than we are usually applying.
Basically, we needed to figure out a design scheme that was both intuitive and engaging. In order to pull that off, we went through a series of tries and fails until we have managed to come up with the most effective and yet minimal solution.
During the development process, we have rearranged and streamlined the entire design scheme to a bare minimum – only those elements that were necessary were left. Everything else was nixed so that the user experience will be absolutely seamless.
Read also: 8 Challenges with Augmented Reality App Development
Technology Stack
- Xcode (the standard instrument for developing iOS mobile apps)
- Cocoa Touch (standard iOS components)
- ARKit (augmented reality framework for iOS)
- Google Maps (well, the map itself)
- Google Places (Google’s API that provides information on nearby places)
Find out What is Tech Stack and How to Pick Best One for Your Project
Our team consisted of:
- Project Manager (manages communications and sets the tasks and priorities, what features are critical at the moment and which can be a part of the next iteration)
- iOS developer (actually develops the mobile app)
- Business Analyst (creates various use cases to think the architecture through and the features that ultimately would have to be developed)
- UX/UI Designer (creates the designs and thinks the user flow through to make sure the users would actually know how to navigate through the app)
Summary
This local restaurant and cafe app for iPhone was a giant leap forward for our company. As first of its kind, it was a gamble that ultimately paid off in a form of a well-made application.
Over the course of the project, our team refined and expanded expertise on the subject of Augmented Reality and geolocation. This gave us several insights which we are eager to apply in future projects. This restaurant finder app was a great learning ground.
Want to receive reading suggestions once a month?
Subscribe to our newsletters