Telemedicine vs. Telehealth: A Comprehensive Guide on the Differences & Benefits
- What is Telemedicine?
- Examples of Usage Medical Services
- What is Telehealth?
- Examples of Telehealth Services
- What is Telecare?
- The Difference between Telemedicine and Telehealth: remote healthcare services
- The APP Solutions Experience: Success Story
- Pros and Cons of Telehealth and Telemedicine
- The Bottom Line
What could be more personal than a doctor’s appointment regarding sensitive information for anyone? Yet, a doctor is one of the few professions required to maintain data privacy. That is why we lock the door when we walk into a specialist’s office.
However, digitalization has reached healthcare over time, and appointments have slowly begun to flow online. COVID-19 added fuel to the fire when face-to-face contact, including in medical facilities, was drastically limited.
Before the pandemic, there was also a range of problems that prevented doctor visits – mismatched patient and doctor gap; low patient mobility; long distances to the hospital; lack of subspecialty doctors or expensive diagnostic and surgical equipment in the nearest county; and expired insurance. These and many others became factors in which visits to the doctor were continually delayed, sometimes with potentially fatal consequences.

Hence, the need lined up to create and rapidly develop web and mobile solutions that would cover the industry’s need for better time management for both the physician and the patient. According to SingleCare, the number of providers offering telemedicine services increased from 19% to 58% during the pandemic. At the same time, according to their data, ¾ of respondents are willing to use telehealth services. Meanwhile, a face-to-face visit would be entirely satisfactory for respondents too.
Achievements in information and communication technology today offer us online visits to the doctor, which are called differently – Telehealth, Telemedicine, and others similar terms… Depending on the context, these terms can be both synonymous and differ in specific nuances. So let’s explore the similarities and contrasts between them.
HEALTHCARE CHATBOT: IMPROVING TELEMEDICINE & ENHANCING PATIENT COMMUNICATION
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine uses digitalized communication technologies to provide various types of medical and diagnostic services, usually provided by physicians or, simply put, treatment at a distance. A term introduced before anything else in its “class.” It is a remote doctor’s appointment that involves both making diagnoses (enabled by such communication) and tracking progress during a patient’s recovery.
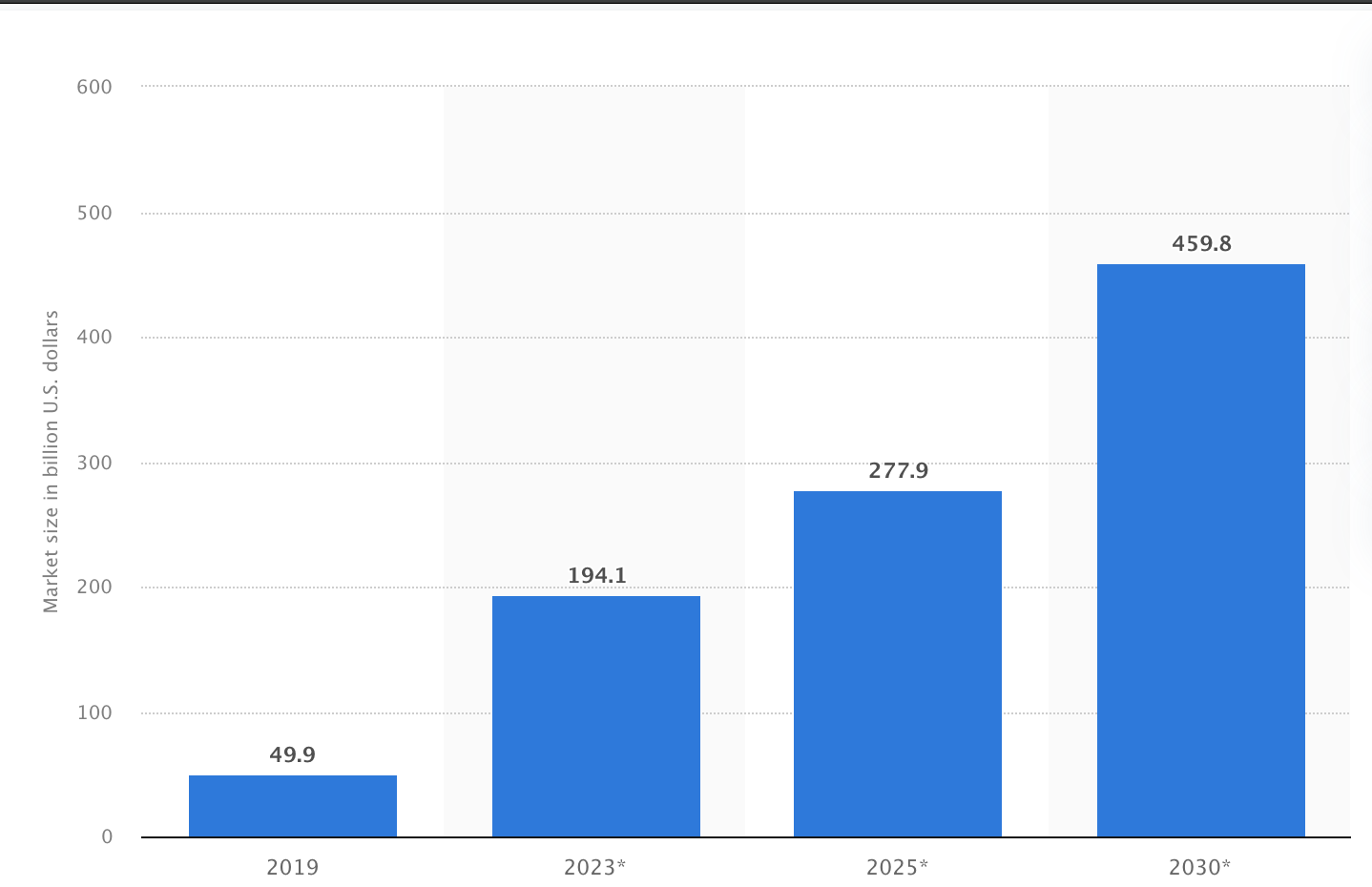
According to Statista, the market is projected to grow significantly by 2030, estimated at nearly $460 billion.
- Alternative to an in-person physical examination (prevention, history taking, diagnosis)
- Distant monitoring (follow-up visits, post-op support)
- Remote clinical services: management of chronic diseases, mental health services
CHOOSING TELEMEDICINE SOFTWARE DURING COVID-19: A COMPLETE GUIDE
What is Telehealth?
Telehealth is a similar term but a broader one. It covers not only medical but also paramedical services (educational, administrative, coaching). That is, it is not only a doctor-patient relationship. The definition also includes nurses, pharmacists, and social workers – all the services they can provide remotely.
For example, programs for professional health-related education of patients, social support, and control over medication adherence. Telehealth also includes so-called asynchronous conferences, when participants do not view data simultaneously and communicate with a “delay.” That is, not in real time, but with saving and forwarding materials. This practice is good, for example, for the consensus of doctors when several experts from different parts of the country have to analyze a patient’s medical history and give their opinion.

- Video Conferencing (patient consultation, webinars for medical staff)
- mHealth (Mobile Health, e.g., an app that alerts the public to health conditions)
- Remote Health Monitoring/ Remote Patient Monitoring (blood pressure, heart rate, weight, blood glucose, and oxygen levels, menstrual cycle)
Thus, the prefix “tele-” does not only refer to video but also any other data in an online format because, from the Greek, “tele” translates as – far away, at a distance.
What is Telecare?
Telecare goes far beyond medicine. Telecare is more about healthy lifestyles in general, that is, how people can control themselves within their non-professional skills. This usually includes consumer-oriented health and fitness apps, sensors and tools that connect users with family members or other caregivers, exercise tracking devices, digital medication reminder systems, and emergency medical alarms for acute deterioration.
There are other, even more, specialized terms, such as teletherapy, telesurgery, telemental health, telescreening, or telemonitoring. Different medical professionals need each of these services in different situations – radiologists, cardiologists, pathologists, dermatologists, nurses, pharmacists, etc.
But they are pretty specific, so we will not focus on them.
A GUIDE ON HOW TO CREATE A TELEMEDICINE APP LIKE DOCTOR-ON-DEMAND
The Difference between Telemedicine and Telehealth: Remote Healthcare Services
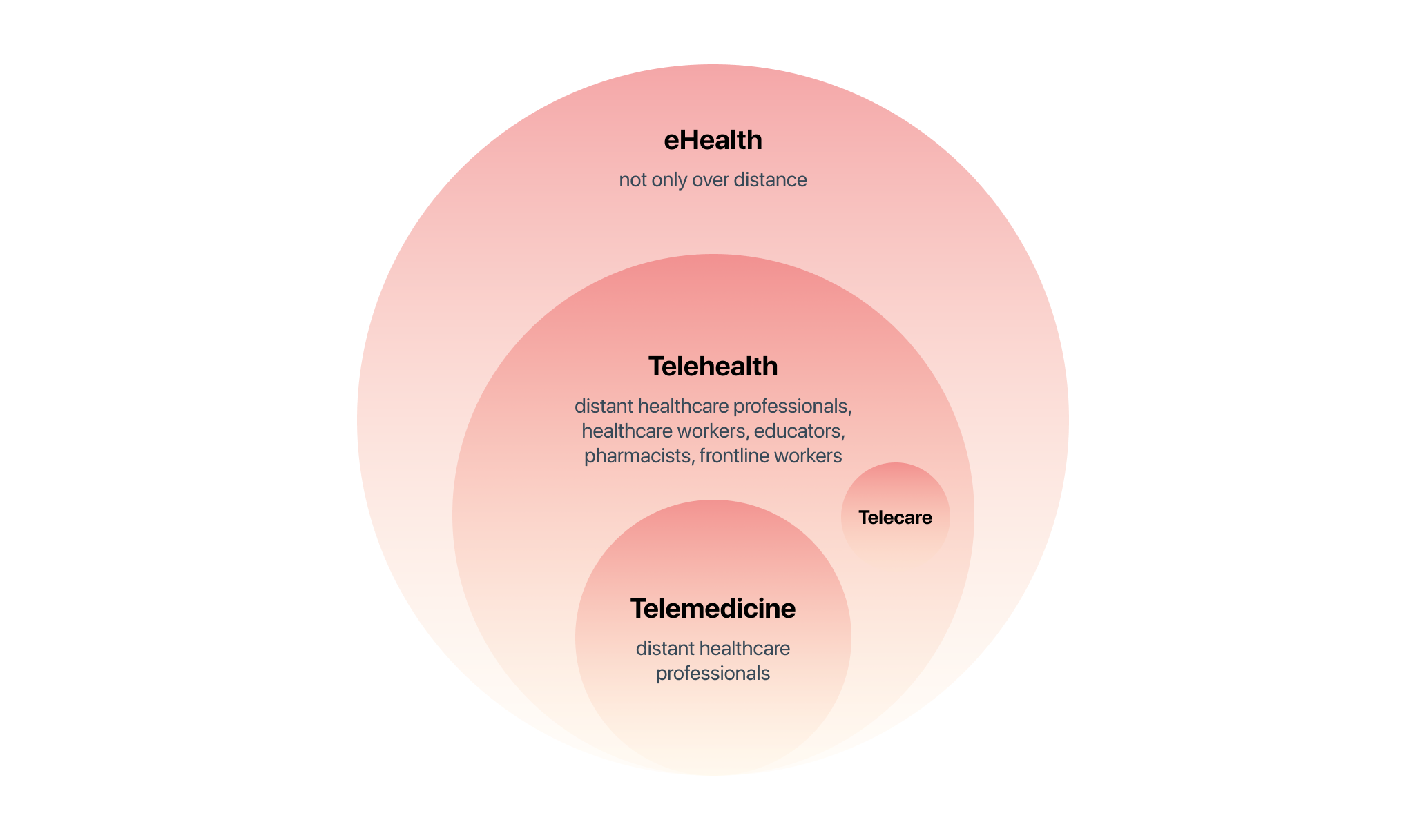
Simply put, telehealth is a subset of telehealth. Technologies commonly used for telehealth include the internet, video conferencing, stored images, streaming media, and wireless communication. Unlike telemedicine, where only healthcare professionals work, telehealth can also include healthcare workers, educators, pharmacists, and frontline workers.
All of these components are part of the substantial eHealth ecosystem, which includes any other digital data in written/photo/audio form, as well as web and mobile apps or cross-platforms. eHealth refers to the combined use of electronic communication and information technology in the healthcare sector to share, store, and retrieve electronic health data for prevention, diagnosis, treatment, monitoring, and educational and administrative meetings, both locally and at a distance.
For example, an electronic health record (EHR) system with telemedicine functionality. Both telehealth and telemedicine require the provider to use HIPAA-compliant software to protect personal health information. This includes protecting video, photos, and data transmitted through telemedicine platforms.
The APP Solutions Experience: Success Story
The client is the owner of a medical center in Berlin, Germany. After the COVID-19 outbreak, he faced the need to provide patients with a distance communication solution to decrease the number of offline visits while enabling doctors to monitor vital patient health data and streamline communication with a laboratory.
After working with us, the client received a white-label telemedicine platform with advanced features that took us two months.
The white-label platform brings benefits to both types of users.
For example, medical professionals can exchange files with patients via secured live chat, send, and receive laboratory tests in a more streamlined way.
Patients can receive high-quality medical services in the comfort of their homes, schedule appointments with doctors, attend medical meetings online, and get receipts for medication and medical treatment plans with a daily schedule. The app also allows patients to pay for medical services online.
HOW TO MAKE EHR/EMR EPIC INTEGRATION WITH YOUR HEALTH APP
Pros and Cons of Telehealth and Telemedicine
- Provides access to a doctor of any profile (from a pediatrician to a speech therapist) for all those who find it difficult to attend an appointment
- Reduces infrastructure costs, increasing profitability
- Optimizes the selection of convenient times for both physician and patient
- Allows for prompt response, diagnosis, and referral to the hospital if necessary (appointments can be made around the clock)
- Reduces the risk of getting infected by other patients in line
- Continuously improves the skills of medical professionals
- Provides as much privacy as possible (which is essential, for example, when visiting a psychiatrist/psychotherapist), provided that the method of communication you choose has a high degree of healthcare cybersecurity
- Difficulty in use by people who are not technologically proficient
- Lack of stable Internet for video sessions
- Unexpected technical glitches in a particular application or solution
- Not every insurance company covers these services
- Quite a significant layer of diagnostic procedures cannot be performed online
Healthcare Apps Development: Types, Examples, And Features
The Bottom Line
Whatever the difference between telehealth and telemedicine, there is no denying their importance in healthcare in the face of the pandemic spread, the overall world population aging, and the significant increase in chronic diseases in societies. The billions of dollars invested in the industry also confirms this.
All the more, there are no absolute and official terms for these concepts anyway.
THE APP SOLUTIONS – CUSTOM HEALTHCARE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT COMPANY
It’s important to monitor your health – both online and offline – by resorting to one method or other in each situation. For instance, you can talk to a psychotherapist via Skype, but you should rush to the hospital at the slightest suspicion of a stroke, not try to call your therapist by video. In any case, either Telehealth or Telemedicine helps streamline time, costs, and the overall win-win situation in the relationship between patients and healthcare providers.
Developing a top-notch teleproduct requires a skilled team to ensure safety, user-friendliness, smooth operation, and mass appeal. As shown above, we have experience in developing telemedicine applications. If you have a thought-out project with a business plan, or even just an idea – send us a message! Our experts will contact you to discuss further steps.
