Healthcare Cybersecurity: how to protect patient data
When people talk about cybersecurity and cybercrime, the first thing that comes to mind is financial fraud and bank security. However, what could be more important than the security of our data in healthcare? After all, it’s not about mundane financial well-being, but our physical condition, and even our lives. And it’s not so much a matter of someone possessing and taking advantage of our health data as it is of a doctor not being able to access such data on time.
This is especially true since healthcare is second only to finance in the interest of cyberattacks. And, the cost of a data breach puts healthcare in the lead (according to HIPAA Journal – $408 per record, compared to about $148 in other areas). In addition, 21% of the consequences result in legal liability, 40% in loss of essential data, and 33% in outages.

STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE ON MOBILE APP HIPAA COMPLIANCE
What is Healthcare Cybersecurity?
Healthcare cybersecurity is an area of information technology aimed at protecting healthcare systems. These systems include electronic health records, health tracking devices, medical equipment, and software to deliver and manage care.
Cybersecurity in healthcare aims to prevent attacks by protecting systems from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure of patient data. The main goal is to ensure the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of critical patient data, which, if breached, could endanger patients’ lives.
However, there is a global shift in health and human services, with more and more of these services being made available online since COVID-19. Accordingly, medical and paramedical processes, and all other areas, began to digitize as quickly as possible, which has happened before but not on such a scale or at such speed. The catalyst, in the form of the coronavirus, has given a significant load of medical professionals not only offline but also online – telemedicine, e-prescriptions, and even remote surgeries. Thus, the need to optimize processes through digitalization has become evident. And when it comes to the secure storage of big data, the question of cybersecurity is bound to arise.
How To Make A Medical App In 2021: The Ultimate Guide
How Common are Cyberattacks in Healthcare?
According to Statista, the industry is expected to be worth $345.4 billion by 2026, up from $34 billion in 2017. In other words, the financial infusion into Healthcare Cybersecurity has increased tenfold in 10 years. Not surprisingly, Statista cites a study showing that in 2020, 17 percent of healthcare cyberattacks caused severe injury or damage to patients, and nearly 30 percent caused disruption of emergency services.
According to the HIPAA Journal, healthcare cybersecurity statistics show an 8% decrease in incidents in February 2022 compared to January 2022. Nevertheless, those 46 incidents affected 2.5 million people. As a result, the healthcare industry has lost $25 billion over the past two years.
The number of breaches and affected people:
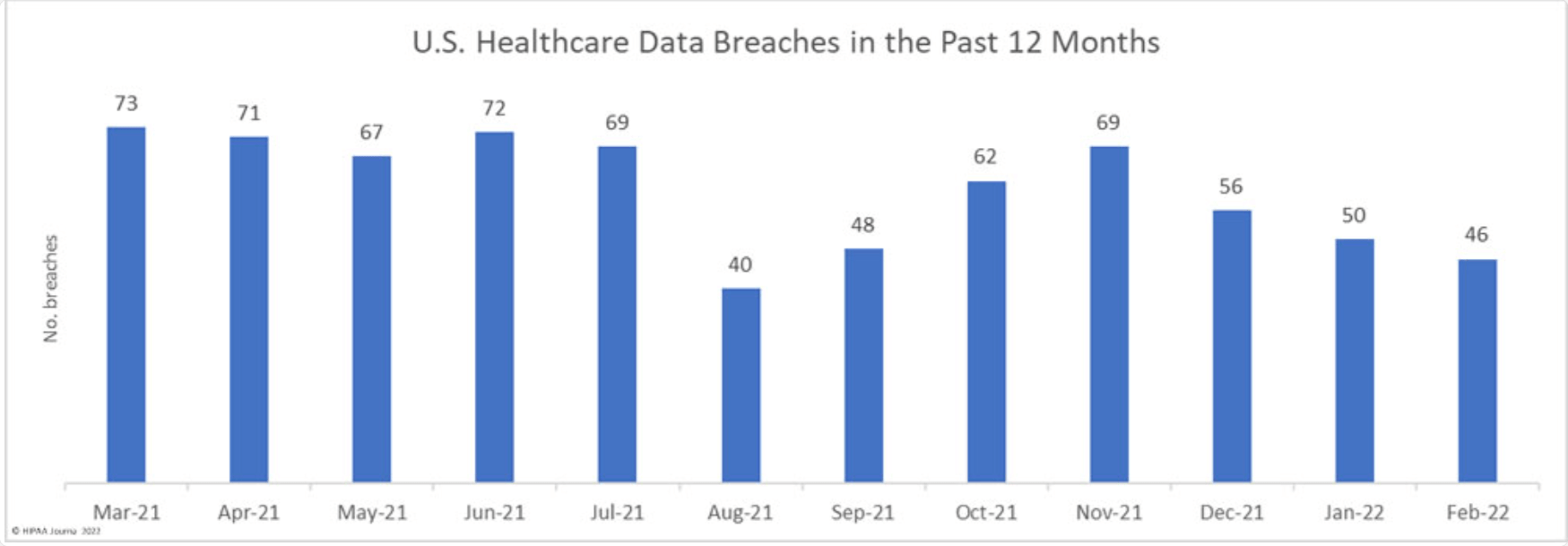
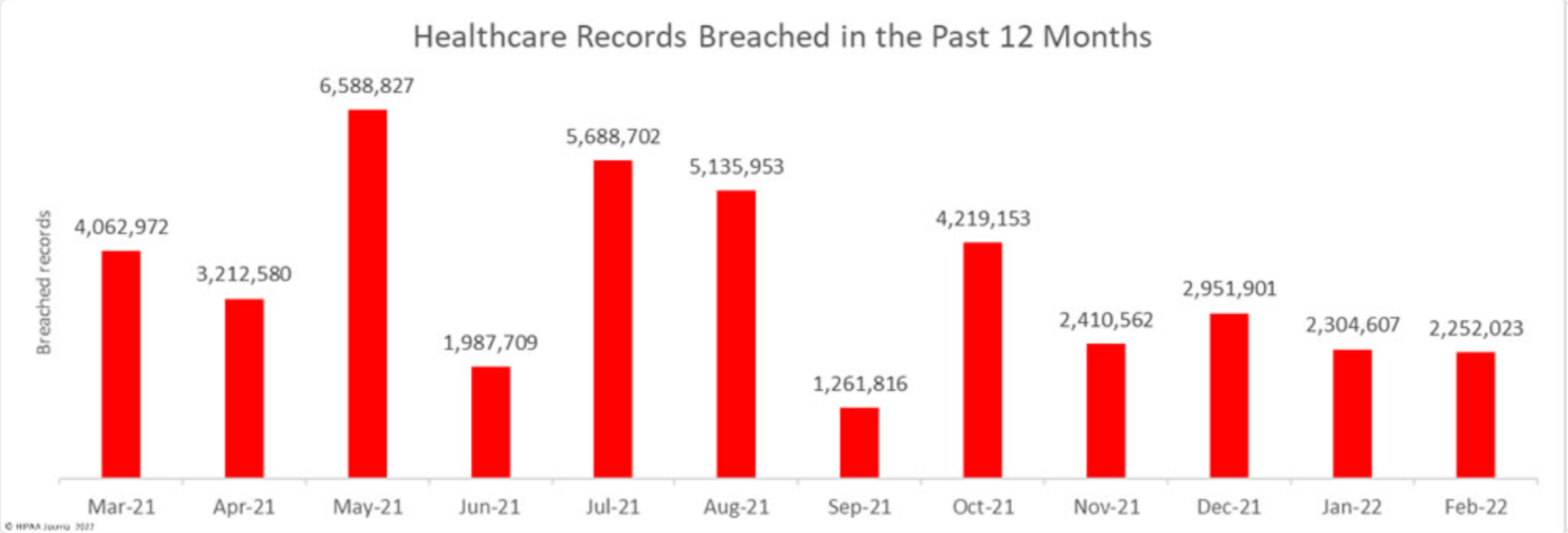
Why is Cybersecurity a Problem in Healthcare?
By far, the most common type of cybersecurity attack is a money-making attack.
In addition to ransomware attacks on financial assets, the industry has seen invasions aimed solely at disruption, as well as attacks aimed at compromising user data. Recently, cybercriminals have been using indirect supply chain attacks to disrupt companies far beyond their original targets.
There is a vigorous public debate that responsible government agencies simply cannot keep up with the scope and “quality” of the threats that must be met. In such an atmosphere, it is every man for himself, and private companies are forced to establish a system of protection on their own without being able to ask for help from government healthcare providers. There is an understanding that it is necessary to work proactively rather than respond to attacks after the fact.
HOW TO INTEGRATE YOUR HEALTH APP WITH EPIC EHR/EMR
The Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022 is designed to help with this, but it is too early to tell if it is effective.
As a result, more than half of the world’s population does not trust healthcare providers to protect personal data. At the same time, in the U.S. the figure is much better – 80%.
The difficulty is that, in any clinic or hospital, there are many networks and digital complexes: EHRs, electronic prescriptions and decision support systems, intelligent heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, infusion pumps, and medical Internet of Things (IoT) devices, etc. All of these can be threatened by cybercriminals.

Related readings:
Calmerry Online Therapy Platform
Orb Health – Сare Management As A Virtual Service
BuenoPR – 360° Approach to Health
Types of Attacks on Healthcare Organizations
Deloitte experts identified several threats faced by many healthcare organizations:
- Phishing. One of the most unsightly, and therefore most common, methods – links or attachments in emails infect computer systems with malware, which then spreads across the clinical network.
- Man in the middle. Cybercriminals infiltrate data transmissions and steal users’ personal information, resulting in severe damages and fines for privacy violations. Sometimes it’s much more trivial – attackers quickly gain physical access to the computer with the data.
- Attacks on network vulnerabilities. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache poisoning, HTTPS spoofing, and other similar cybercrimes targeting wired and wireless networks that provide access to patient information.
- Ransomware attack. Criminals not only encrypt data and extort money for decryption, but also block access to the entire clinical system, paralyzing surgical and life-support equipment.
- IoT attack. Personal patient information and high-tech connected medical devices used in invasive and noninvasive procedures can be attacked, as well as auxiliary equipment not directly related to medicine – smart elevators, intelligent heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, and infusion pumps.
Healthcare Cybersecurity Challenges
Indeed today, there is no medical institution that is not protecting the personal data of its patients, as they are required by law to do. But, undoubtedly, one of the most important challenges in this situation is the backwardness and complete irrelevance of such protection. Sometimes the so-called cybersecurity of an individual hospital can be compared to a cardboard wall that shields itself from a fire-breathing dragon.
The reasons for this may be different – from the inability to allocate an adequate budget for protection to the banal connivance – “it won’t affect us.”
One of the factors of such a challenge can be considered the forced pulling of your medical institution/company to the super modern standards of cybersecurity. Otherwise, no insurance company will want to cooperate with you to avoid their losses from attacks on you.

Healthcare Mobile Apps Development: Types, Examples, And Features
How to Improve Cybersecurity in Healthcare
To make the number and possibilities of cyber attacks less and less possible every year, you need to work systematically on the process of building your security. Cybersecurity solutions include endpoint protection, identity access control, data protection, and network security. These technologies are used to protect sensitive information and critical systems from attack. More specifically, these measures aim to protect against threats from inside and outside the organization. This underscores the need to view cybersecurity as a comprehensive strategy consisting of practices and technologies.
What solutions can we offer?
Find Out More
Thus, it is first important to implement technology and collect analytics regarding the frequency and nature of cyberattacks so that a preventive level can be triggered later. In parallel, fundamental security should be in place in any business or government institution related to the protection of citizens’ data – from the tax office to the online lingerie store – should not be forgotten. Organizations should adopt modern security measures, including multifactor authentication and privileged access management, to create a threshold level of security.
Another effective measure should be cybersecurity training for all staff from the lowest to the highest levels (hopefully, no one keeps their account password on paper under their laptop anymore) – how to keep themselves safe; which links to click and which not to click; which emails to open and which not to. How often to backup data and make software updates, what passwords should be, what is multifactor authentication, and what to do if a hacker attack still occurs.
We would like to remind you that about a third of all data leaks are due to human factors – deliberately or not, an employee of a healthcare institution gives out the necessary data to malicious insiders. Of these types of leaks, twice as many are unintentional. In other words, the culprit is trivial human negligence.
Clinics must control and monitor malicious file activity. To do this, they can implement systems that block unauthorized actions with data, prevent unauthorized email exchanges, prohibit the possibility of copying to external sources, etc. Unfortunately, the institution doesn’t find out about 39% of hacks until a month later; this situation needs to change urgently.
Finally, endless testing is essential – APIs must be thoroughly tested before they can be trusted in healthcare systems to enable data sharing while maintaining internal security measures.
Conclusions
As times have changed, healthcare systems must change with them, which means more than just annual risk assessments and periodic tests. Each year we come to an increasing realization that the modern hospital is not just physicians and nursing staff, but also a complex system designed to automate, optimize, and store databases, integrated with pharma, biotech government, insurance, and financial entities. Breaking into this system would result in hours to weeks of paralysis, which is unacceptable due to the nature of the industry.
As we advance, organizations and their technology partners must take responsibility for implementing robust, thoughtful technology and procedures, as well as regular testing and validation of systems. These measures are the best way to meet today’s cybersecurity requirements while preparing organizations for future events.
THE APP SOLUTIONS – CUSTOM HEALTHCARE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT COMPANY
These frameworks focus on:
- Describing the security situation and communication risks
- Identifying methods for dealing with cyber threats
- A plan for continuous improvement
Obviously, it’s too costly and impractical for the smallest medical center to keep its own cybersecurity staff. It’s better to outsource that kind of responsibility and not have to worry about anything. But to do that, you have to find professionals you can trust.
The APP Solutions can find you a team of specialists who will protect against cyberattacks, regardless of the complexity of the product you need to secure.
Credits to Depositphotos
Did you come up with something?
Calculate The Cost
