Step-by-step guide on mobile app HIPAA compliance
Mobile applications have changed our world over the most recent couple of years. Also, with the growing health care sector, a mobile app is a vital segment for both specialists and patients. An ever-increasing number of individuals are utilizing online media and web administrations in numerous aspects of their lives. New technologies, from electronic medical records and medical devices to mobile and web applications, allow doctors to improve patient health and save lives.
Those companies that do not conform to the HIPAA rules will hit it hard with their clinical software. This makes this legislation the most principal government law for any dev who represents considerable authority in making mHealth software for US customers. Building up a health-related app is arduous itself, not to mention making it HIPAA-compliant. Nonetheless, it is vital to feel comfortable around it since the penalties for abusing the enactment are colossal.
TOP 10 HEALTHCARE TRENDS EXPECTED TO BE IN 2023

Building an app for health care may come across as a simple undertaking. All you have to do is locate a patient or clinician, assemble a dev group, and immediately tackle a significant health care issue. However, it doesn’t boil down to that.
Security infringement in the human administration division presents major issues with critical budgetary outcomes. Practically 90% of clinical administrations in America have encountered information leaks with assessed misfortunes of $6.2 billion. And that is where app HIPAA compliance comes in.
HOW TO CREATE A MEDICAL APP: THE ULTIMATE GUIDE

[Source]
What Is HIPAA?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a governmental regulation that settles rules for sharing personal health information and preventing unsanctioned use.
The HIPAA Act is based on two important ideas in patient care: privacy and confidentiality. The legislation was intended to protect people from losing their health insurance if they change employment or have any health conditions. The act has been expanded several times, as it was written many years ago in the non-digital world. In general, this notable law provides the following:
- Insurance portability
- Standardization and efficiency in health care data
- Avoidance of fraud and discrimination
- Among other things, HIPAA has arrangements for the security and privacy of PHI (personal health information)
HEALTHCARE CYBERSECURITY: HOW TO PROTECT PATIENT DATA
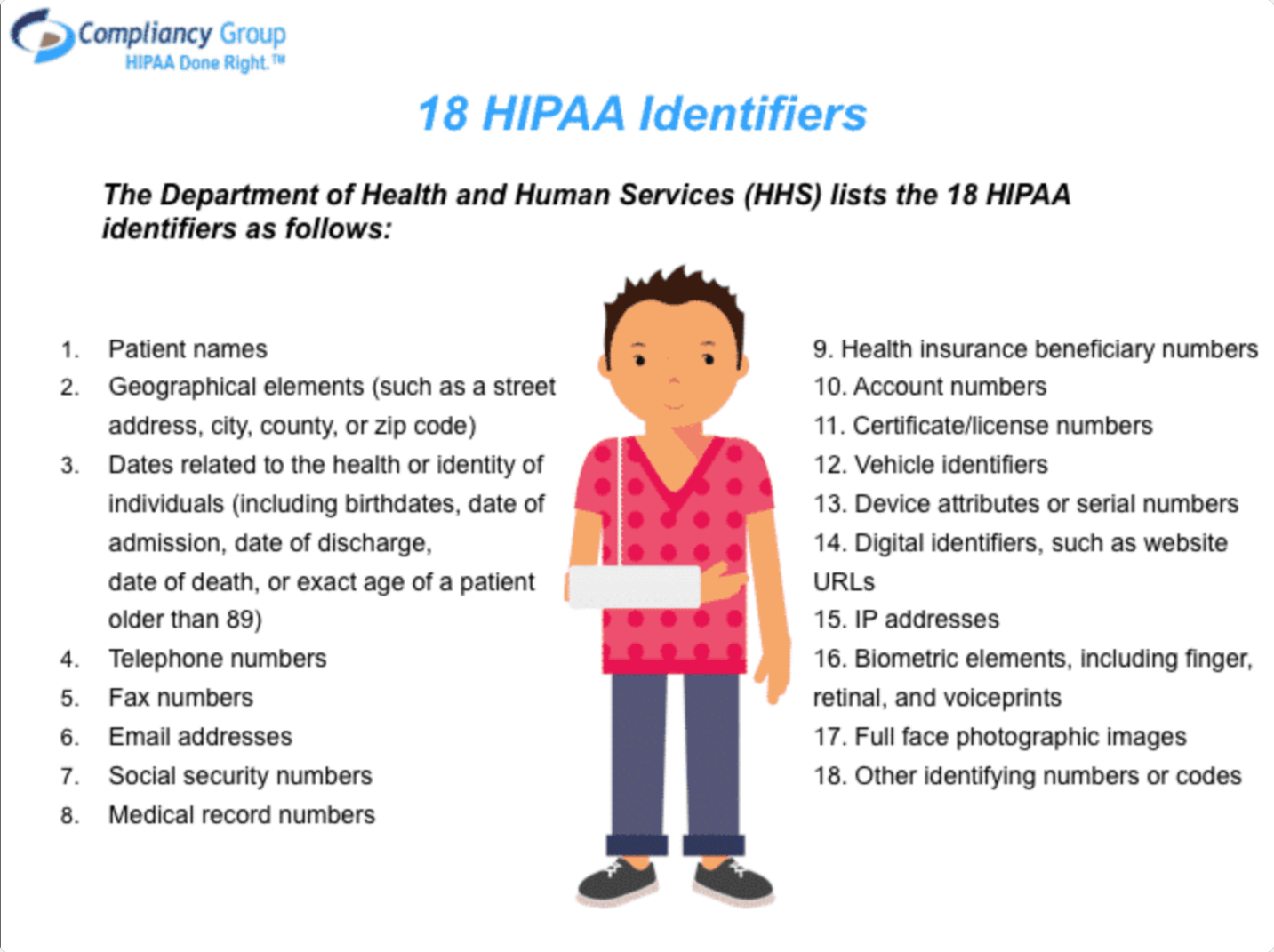
HIPAA requirements are identified with foundations secured by the law: emergency clinics, corporate medicinal services associations, research establishments, and insurance agencies that manage patients and their data. The HIPAA PHI security necessity likewise applies to partners of these offices.
Related reading:
The HITECH law, established in 2009, enhanced the existing HIPAA policies. HIPAA and HITECH mutually set a lot of administration security principles to ensure PHI protection. These arrangements are remembered for purported managerial disentanglement rules. HIPAA and HITECH characterize the necessities for the utilization and exposure of PHI, suitable PHI security measures, rights, and authoritative commitments.
But why is HIPAA compliance imperative for an app? To answer this question, it’s enough to have a look at mobile health applications court cases. If a company does not scrutinize the security risks, it may end up paying monstrous fines and lose its reputation. On average, a stolen medical record can cost around $20, which is 20 times more than credit card data. To forestall identity theft, blackmail, and scam, all social insurance applications in the US need to meet the HIPAA requirements.
HOW TO MAKE EHR/EMR EPIC INTEGRATION WITH YOUR HEALTH APP

According to the level of carelessness, there are four tiers of HIPAA fines, which vary from no fine to $50,000. The latter refers to the most serious breach.
Emerging Best Practices for HIPAA-Compliant Mobile Apps in 2025
Staying compliant with laws and regulations is the only way to operate legally in every sector, with the health industry being no exception. Actually, it is here where legitimacy plays a crucial role in business success, helping it build trust and credibility while avoiding huge fines. Here are three best practices that every company in the niche must adopt:
Integrate zero-trust architecture. The approach of “never trust, always verify” is becoming increasingly popular among companies as it goes beyond perimeter security and ensures validation and authorization of every process.
Adopt AI-based threat detection. AI and ML are great at analyzing anomalies in real-time, surface security holes, and possible breaches that malicious actors could exploit.
Maintain a continuous compliance mindset. Ensuring compliance is not a one-time thing. Use CI and CD pipeline to introduce automated HIPAA checks throughout the product’s lifecycle.
HIPAA Terminology
Before we dive into the HIPAA requirements, let us deconstruct HIPAA compliance terminology:
- Protected health information (PHI) – any individually identifiable data.
The PHI term covers a wide range of personal health information, such as insurance and payment information, diagnosis, clinical care, and examination results such as images and tests. The data can be created, stored, or transmitted in many formats through verbal conversations, written documents, computer software or hardware, and various other forms. Everything requires security and confidentiality measures to be implemented.
RPA IN HEALTHCARE: A COMPREHENSIVE OVERVIEW, BENEFITS, AND USE CASES
PHI may include anything in the patient’s health information such as lab results, medical history images, and more. It also refers to other personal records like name, date of birth, SSN, and other information that can be used to create identity theft. It seems like every day we hear about another data breach, so PHI disclosure is deemed one of the major issues. Taking care of patient information falls under the HIPAA guidelines.
Need help in developing your Healthcare App?
Reach out
- Covered Entities – associations and people offering healthcare services/activities or accepting payments for them.
The HIPAA rules are applicable to covered entities HIPAA as well. Covered entities incorporate health care suppliers, information centers, and plans. If we are talking about healthcare providers, these refer to specialists, clinics, hospices, pharmacies, and other providers. A person or organization is considered to be a healthcare provider if they pass on any information in an electronic form regarding a transaction for which HHS has set a standard. Clearinghouses are HIPAA-covered entities that handle nonstandard HI they receive from another entity into a standard. As for healthcare plans, these include insurance companies, company health plans, etc. and are regarded as covered entities HIPAA as well.
WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN HEALTHCARE?
- Business Associate – the nonmembers that work as vendors or subcontractors for a covered entity with PHI admittance.
When a covered entity draws in a business associate to assist it with completing its social insurance activities, the covered entity must have a composed business associate contract or plan with the business associates that establishes the business associate’s accountability. Sample HIPAA policy and procedures for business associates are accessible on the web. HIPAA for business associates, in this case, covers PHI privacy and security procedures. Notwithstanding these legally binding commitments, HIPAA business associates are accountable for consistency with specific arrangements of the HIPAA Rules. Some companies even offer HIPAA training for business associates.

Health Applications Use Cases and HIPAA
Logically, there may arise a question – do all health apps need to abide by HIPAA? Well, the answer is in the information source and the aim of data gathering. According to HIPAA guidelines, Protected Health Information (PHI) expands to the data built or collected by a covered entity. It identifies with the past, present, or future mental or physical wellbeing of a person, just as any data that relates to the person. Hence, some app developers may need to create an app HIPAA compliant and pay special attention to the Security Rule. Let us have a closer look at health applications cases and HIPAA-compliant mobile apps.
[Source]
When healthcare mobile applications are subject to HIPAA
Needless to say, profound knowledge of your application use cases is essential. It is especially crucial to realize whether or not your mobile apps will store or transmit PHI even if the collected data doesn’t fall under HIPAA by itself.
MICROSOFT CLOUD FOR HEALTHCARE: HOW MS CLOUD SOLUTIONS ARE BENEFITING HEALTHCARE ORGANIZATIONS
As soon as protected health information appears on mobile apps, they must become HIPAA compliant apps. A basic example of a HIPAA compliant mobile app is a HIPAA compliant mobile scanning app since it is used to transfer a patient’s data. Now let’s explore HIPAA-compliant phone apps in more detail.
Telemedicine (doctor-on-demand) apps
As you can guess, telemedicine and HIPAA compliance go hand-in-hand. The main purpose of HIPAA-compliant telemedicine software is to protect privacy and provide fool-proof security of patients. Also, telemedicine HIPAA compliance makes sure you won’t get heavily fined for protected health information leakage. The main telemedicine HIPAA requirements touch upon authorized access, secure communication, and a system of monitoring.
The HIPAA guidelines on telemedicine are counted in the HIPAA and Telemedicine Security Rule.
EHR apps
Mobile EHR apps allow your health care professionals to take digital notes as opposed to paper-based ones. HIPAA and EHR apps guarantee privacy, unification, and accessibility. When HIPAA EHR apps receive patient data from a covered entity, the EHR system developer may be accountable for EHR HIPAA compliance for ensuring forbidden use or exposure of the ePHI.

As for the relationship between EHR reimbursement, HIPAA, and EDI Transactions, EHR relates to the client and health data entered into the computer. Whereas, EDI Transactions are the manner by which this data is traded between various offices and the insurance. Thus, EHR and HIPAA combined to take care of patient’s clinical records and other health information, including health plans, doctors, hospitals, and other human services suppliers.
WHAT IS EHR (ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORD), AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
Condition-based apps
A medical app must also be HIPAA liable if it features protected health information, including the patient’s physical or mental conditions, and healthcare services. This is also true for mobile apps that include past, present, or future payments for the provision of care.
When mHealth apps do not fall under HIPAA
The majority of mobile apps do not fall under the scope of HIPAA compliant apps, as they are made for personal use only and do not feature any information that can identify the patient. Examples of non-PHI apps include:
Workout programs apps
If mobile app stores such data as calories burned, weight loss information, it doesn’t have to be HIPAA compliant.
Diet apps
A mobile app that manages a daily food diary, tracks activities, and weight loss progress, doesn’t count as PHI as well.
IoT Fitness apps
An IoT-enabled fitness app collects and delivers data that can be used to track personal growth. Hence, an IoT mobile app doesn’t have to comply with HIPAA requirements.
When HIPAA is being used Wrong?
For more information visit: PODCAST #5. EMPOWERING EXPERTISE: HOW TO THRIVE AS A SCARCE SPECIALIST IN B2B
or watch our podcast, CareMinds, where you can hear from respected experts in healthcare and Health Tech.
I want a free consultation for my Healthcare project
Contact Us7 steps to apply HIPAA to your mobile app
As usual, compliance with HIPAA is an expensive affair for most m-health app makers. Surely, there exist various services like a HIPAA compliant app builder that can create HIPAA compliant iPhone apps within minutes. But, it is necessary to know your way around the law, as it guarantees full HIPAA compliance for software development. To meet HIPAA prerequisites, you have to take all essential authoritative, physical, and specialized measures to ensure individual clinical information such as protection, reliability, and security of electronically communicated PHI.
Administrative safeguards refer to access control and training, physical safeguards refer to servers, data centers, PCs, laptops, etc., and technical measures entail the health data itself.
MICROSOFT CLOUD FOR HEALTHCARE: HOW MS CLOUD SOLUTIONS ARE BENEFITING HEALTHCARE ORGANIZATIONS
Additionally, the process of building a HIPAA-compliant phone app presupposes IT risk analysis. However, there is no comprehensive information about it in the HIPAA Security Rule. But, a number of documents help understand HIPAA requirements better and ensure sufficient risk assessment procedures.
Based on these documents, we’ve put together 7 steps for ensuring HIPAA compliance for your business. These instructions also provide a closer look at comprehensive HIPAA risk analyses in 7 steps.
Step 1. Get Access control
An HIPAA compliant app that stores PHI should impose restrictions on who can see or alter confidential information. As indicated by the HIPAA Privacy Rules, no one should see more patient health information than required to carry out their responsibility.
Step 2. Secure Person or entity authentication
The next thing to do after assigning app privileges is to know exactly who is accessing PHI. The law offers the following authentication methods for HIPAA compliant software development:
- Biometrics (for example a unique mark, a voice or face ID)
- Password
- Physical methods for distinguishing proof (for example a key, card, or token)
- Personal Identification Number (PIN)
AGILE HEALTHCARE: HOW TO IMPLEMENT THE APPROACH
Step 3. Ensure Transmission security
Transmission security guarantees that PHI being transmitted over the app network is encrypted during transmission.
The HTTPS protocol, for example, encrypts information with SSL/TLS. With the help of a unique algorithm, it transforms personal health information into a series of characters that is inane without decryption keys.
Try to use it for all your communications, or at least for the signup screens, all pages containing PHI, and authorization cookies.
Step 4. Use proper PHI disposal
Among other HIPAA requirements for software is PHI disposal. Disposal presupposes destroying PHI when it is no longer needed. Make sure there are no copies in any backups; otherwise, the information cannot be considered disposed of. Hence, preventative measures must limit incidental and avoid prohibited uses and disclosures of PHI, including in connection with the disposal of such information.
Step 5. Ensure Data backup and storage
No matter how reliable the HIPAA app storage system is, there is no absolute protection. Also, only a timely backup can help avoid most problems associated with data loss. Data backup refers to creating a full copy of information on another medium. Ideally, the backup should be located on a server, which is located in another data center. This is the only way to guarantee maximum data security on the app.
Step 6. Evaluate Audit controls
An IT audit is an essential step on the way to HIPAA compliance software development. The absence of audit controls in an HIPAA application could prompt higher fines. It would be best if you screened what is done to the PHI stored in your app. Record each time a client signs all through your framework. You should be aware of all operations done with sensitive information within HIPAA mobile apps.
Checking is possible through programming, equipment, or procedural methods. A straightforward option would be to use a table in a database or log file to record all the interactions with patient information.
THE APP SOLUTIONS – CUSTOM HEALTHCARE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT COMPANY
Step 7. Apply Encryption
Encryption is a key way to protect information from intruders. It allows transmitting the data over a network without risks and guarantees data integrity. Encryption is indispensable in the modern digital world, including HIPAA requirements for mobile devices and HIPAA compliance for web applications. All existing encryption methods are based on cryptography, which is the science of message security. Of course, modern methods are not just character conversion and are used not only in personal correspondence. Today it is required to work with absolutely all types of data that are used in the business sphere. Without encryption, the information stored on a HIPAA compliant app can easily be read by hackers.
Corporate data can be leaked when sending information over the Internet, and when copying files. A breach is also possible during unauthorized implementation, and due to unintentional mistakes of personnel. In any of these cases, encrypting data on the app ensures its invariability and complete security, as decryption is most often simply impossible for cybercriminals.
Download our Free Healthcare app eBook
Download